Chiller
- Home
- /
- Technical Information
- /
- Chiller
In vehicles that use the electric battery as their main energy source—such as hybrid, plug-in hybrid, or fully electric vehicles—a new component called the “CHILLER” has been introduced.
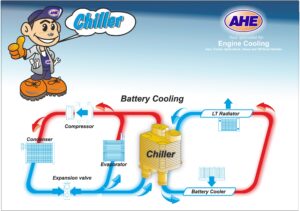
The CHILLER is a heat exchanger specifically designed to cool the fluid that reduces the temperature of the electric battery pack.
The CHILLER is manufactured by assembling plates that are subsequently brazed together. Inside these plates flows the coolant of the battery pack, whose heat is dissipated through internal fins.
Since the CHILLER is generally located inside the vehicle, this heat exchanger cannot rely on ambient air for cooling. For this reason, the refrigerant gas from the air conditioning system is used. Consequently, the design of this component involves a dual-circuit system: one circuit carries the coolant from the battery pack, and the other carries the refrigerant gas from the air conditioning system, which removes the heat.
The appearance of the CHILLER is therefore very similar to that of an engine oil cooler, as both operate on the same dual-flow principle: coolant/oil in the case of the oil cooler, and coolant/refrigerant gas in the case of the CHILLER.
Battery pack temperature control in electric vehicles is essential to ensure both safety and efficiency. Excessively high temperatures accelerate battery degradation, reduce service life, and may cause dangerous overheating with potential fire risks. On the other hand, excessively low temperatures slow down chemical reactions, reducing efficiency and performance.
A thermal management system keeps the battery within the optimal operating range of 15–25°C, maximizing lifespan, safety, and driving range. For this reason, the CHILLER—together with other components dedicated to temperature control—will play an increasingly important role in the future.